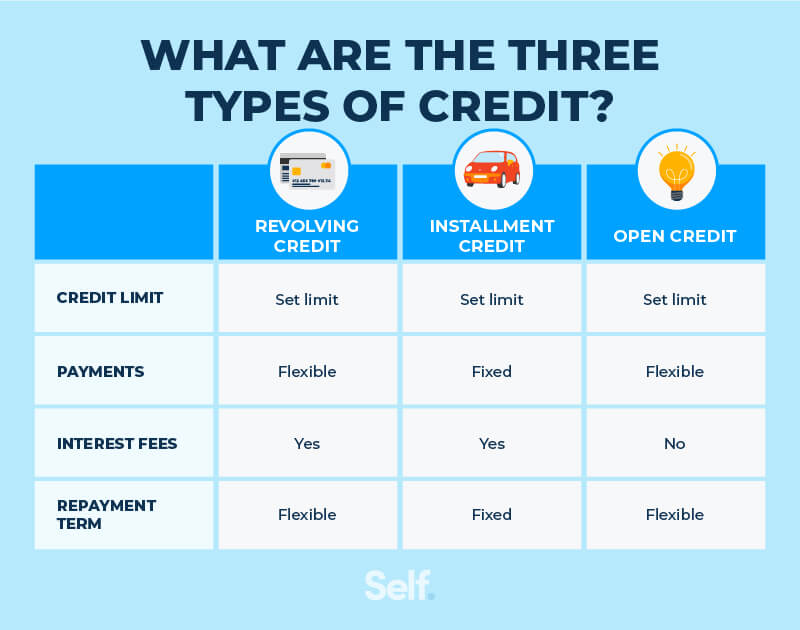
Revolving, instalment, and open accounts are all forms of credit. Depending on the duration of the period (fixed or indefinite), the payment (fixed or variable), and the monthly amount due, these forms of credit might differ greatly (full balance or minimum). Your credit score is built up of 10% of your entire credit mix, which is why it’s preferable to maintain a diverse credit portfolio.
What are 3 types of credit?
Open Credit
There are two types of open credit: charge cards (as opposed to credit cards) and utility accounts. Both accounts need to be paid in full, although they operate in distinct ways otherwise. Unlike revolving credit cards, charge cards are for one-time use only. Charge cards may or may not have fixed credit limits, depending on your qualifying characteristics and how the card is provided. By the end of the next month, you must pay the whole amount you owe. To avoid costly fines or the closure of your account, you must comply. Open credit may also be found in utilities, more especially in the form of service credit. An electric provider, for example, offers you service right away. The fee of the service is then due on the next due date. Utilities require you to pay the whole amount due at the end of the billing cycle.
Revolving Credit
Credit cards are a common kind of revolving credit for most individuals. Home equity lines & Personal lines of credit are two further examples of these types of loans. When you use revolving credit, the total amount you may borrow is known as your credit limit. When you make use of your credit card to purchase, the creditor sets a monthly payment amount that you must meet until the balance on your account is zero. You have the option of making a full payment or only the minimum to avoid late fees.
Carrying a balance on a credit card, on the other hand, means paying interest on the money you owe, and credit card interest rates are notoriously high. If at all feasible, make the last payment to settle the account. Once you’ve over your credit limit, you won’t be able to use your credit card until you pay down the debt. Any fees, late charges, cash advance fees, or balance transfer fees that you incur as a result of making partial monthly payments will be added to your new balance.
Instalment Credit
Instalment credit is most commonly associated with auto loans and home equity loans. You take out a loan for a predetermined sum and then pay it back over a predetermined period of time. The loan will be paid in full at the conclusion of the agreed-upon period if you pay the agreed-upon monthly payment. Making greater monthly payments may allow you to pay off the debt sooner. Saving money by paying off the loan early might help you avoid paying interest, which is charged on a daily basis. Paying off your debt early will save you money in terms of interest payments over time.



![Ghibli Image to Video Generator [100% FREE UNLIMITED CREDIT] maxresdefault](https://ashvircreations.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/maxresdefault-320x179.jpg)




